Getting Started¶
We’ll start by running a simple test workflow, exploring it via the web interface, and terminating it. Then you’ll be ready to start learning how to write your own.
Execute an Example Workflow¶
The console will generate a lot of output as the workflow runs. This workflow tests out various features of Cosmos. The number beside each object inside brackets, [#], is the SQL ID of that object. Clone the git repository so that you have access to the examples code:
$ git clone https://github.com/Mizzou-CBMI/COSMOS2 Cosmos
$ cd Cosmos/examples
$ python ex2.py
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:48: Rendering taskgraph for <Workflow[1] test> using DRM `local`, output_dir: `/locus/home/egafni/projects/Cosmos/examples/out/test`
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:48: Committing 10 Tasks to the SQL database...
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:48: <Stage[1] Echo> Has not been attempted
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:48: <Stage[2] Cat> Has not been attempted
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:48: <Stage[3] WordCount> Has not been attempted
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:48: Skipping 0 successful tasks
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:48: Executing TaskGraph
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:48: <Stage[1] Echo> Running
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:48: <Task[1] Echo {'word': 'hello'}> Submitted to the job manager. drm=local; drm_jobid=15911
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:48: <Task[10] Echo {'word': 'world'}> Submitted to the job manager. drm=local; drm_jobid=15921
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:49: <Task[1] Echo {'word': 'hello'}> Finished successfully
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:50: <Stage[2] Cat> Running
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:50: <Task[2] Cat {'word': 'hello', 'n': 1}> Submitted to the job manager. drm=local; drm_jobid=15931
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:50: <Task[3] Cat {'word': 'hello', 'n': 2}> Submitted to the job manager. drm=local; drm_jobid=15942
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:50: <Task[10] Echo {'word': 'world'}> Finished successfully
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:50: <Stage[1] Echo> Finished successfully
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:50: <Task[8] Cat {'word': 'world', 'n': 1}> Submitted to the job manager. drm=local; drm_jobid=15953
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:50: <Task[9] Cat {'word': 'world', 'n': 2}> Submitted to the job manager. drm=local; drm_jobid=15961
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:51: <Task[2] Cat {'word': 'hello', 'n': 1}> Finished successfully
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:51: <Stage[3] WordCount> Running
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:51: <Task[5] WordCount {'word': 'hello', 'n': 1}> Submitted to the job manager. drm=local; drm_jobid=15975
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:51: <Task[3] Cat {'word': 'hello', 'n': 2}> Finished successfully
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:51: <Task[4] WordCount {'word': 'hello', 'n': 2}> Submitted to the job manager. drm=local; drm_jobid=15986
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:51: <Task[8] Cat {'word': 'world', 'n': 1}> Finished successfully
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:51: <Task[9] Cat {'word': 'world', 'n': 2}> Finished successfully
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:51: <Stage[2] Cat> Finished successfully
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:51: <Task[7] WordCount {'word': 'world', 'n': 2}> Submitted to the job manager. drm=local; drm_jobid=15997
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:51: <Task[6] WordCount {'word': 'world', 'n': 1}> Submitted to the job manager. drm=local; drm_jobid=16005
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:52: <Task[5] WordCount {'word': 'hello', 'n': 1}> Finished successfully
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:52: <Task[4] WordCount {'word': 'hello', 'n': 2}> Finished successfully
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:52: <Task[7] WordCount {'word': 'world', 'n': 2}> Finished successfully
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:52: <Task[6] WordCount {'word': 'world', 'n': 1}> Finished successfully
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:52: <Stage[3] WordCount> Finished successfully
INFO: 2014-09-02 19:30:52: <Workflow[1] test> Finished successfully, output_dir: /locus/home/egafni/projects/Cosmos/examples/out/test
Launch the Web Interface¶
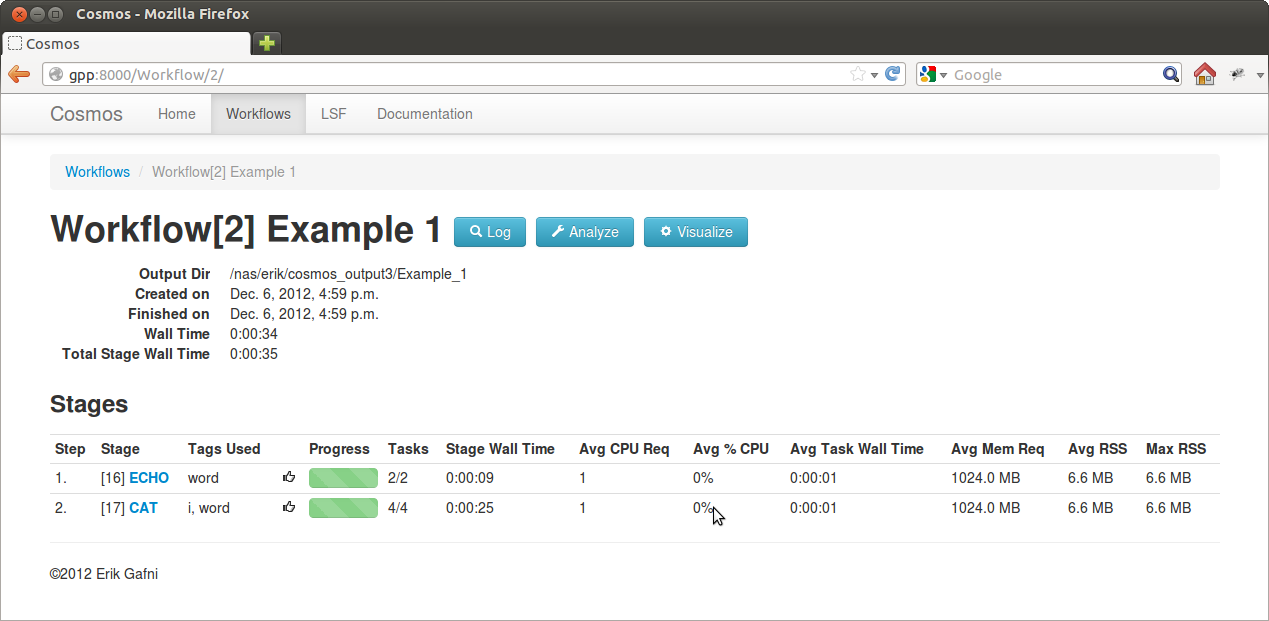
You can use the web interface to explore the history and debug all workflows. Features include:
Visualizing all jobs as a dependency graph (not useful if there are too many jobs)
Visualizing the stages as a dependency graph (high level overview)
Search for particular tasks based on their params or other attributes
See resource usage statistics
For any task, view the exact command that was executed, stdout, stderr, resource usage, inputs/outputs, dependencies, etc.
cosmos runweb sqlite.db
Visit http://servername:8080 to access it (or http://localhost:8080 if you’re running cosmos locally.
Hint
If the cosmos webserver is running, but you can’t connect, it is likely because there is a firewall
in front of the server. You can get around it by using ssh port forwarding, for example:
$ ssh -L 8080:servername:8080 user@server.
Warning
cosmos runweb uses the Flask development webserver which is NOT secure. If you need it secured, you’ll have to set it up in a production Flask web server environment, see Deploying Flask. For example, you can use gunicorn ‘cosmos.web.gunicorn:make_app(“sqlite:///examples/sqlite.db”)’ -w 6 -b 0.0.0.0:3232
Terminating a Workflow¶
To terminate a workflow, simply press ctrl+c (or send the process a SIGINT signal) in the terminal. Cosmos will terminate running jobs and mark them as failed. You can resume from the point in the workflow you left off later.
Resuming a workflow¶
A workflow can be resumed by re-running the script that originally started it. The call to Cosmos.start() will delete any failed Tasks.
Calls to Workflow.add_task() will check the database to see if the Task already has been successfully completed (using the stage_name and uid). If so,
it’ll return the database version of that Task, and not re-run it when Workflow.run() is called. If the Task had failed, Workflow.add_task() will
return a new Task which will be run when Workflow.run() is called.